醫學上「細胞死亡」的兩種情況:「壞死」(Necrosis)「凋亡」(Apoptosis)。「壞死」的情況是像以鐵鎚敲自己的手敲爛,而「凋亡」則是像蝌蚪成為青蛙時尾巴的自動消失。所以「凋亡」是一種有計畫的死亡(消失),和「壞死」大不相同。此外,「凋亡」組織的細胞,細胞膜是萎縮而非像「壞死」那樣,細胞受損而破裂,也因此不會有內含物漏出的情況,引起發炎反應。
Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components.
In contrast,
apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death.
While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal.
[2]
Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated, and result in the loss of
cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the
extracellular space.
[1]
This initiates in the surrounding tissue an
inflammatory response which attracts
leukocytes and nearby
phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by
phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would create collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
[3] This excess collateral damage inhibits the healing process. Thus, untreated necrosis results in a build-up of
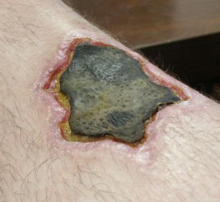
decomposing dead tissue and cell debris at or near the site of the cell death. A classic example is
gangrene. For this reason, it is often necessary to remove necrotic tissue
surgically, a
procedure known as
debridement.

Structural changes of cells undergoing necrosis and
apoptosis
維基百科,自由的百科全書
跳至導覽跳至搜尋
壞死(
英語:Necrosis),又稱
細胞壞死,醫學術語,指細胞或活體
組織因為非正常原因造成的永久性死亡。
它跟
細胞凋亡不同,細胞凋亡是細胞正常性的死亡,通常對生物的身體或成長是有益的。但是壞死通常是指因外在因素造成非正常、病理性的細胞死亡,它會造成疾病,甚至個體死亡。
英語:Necrosis的字根來自
希臘語:
νεκρός,是死亡的意思。